
What is ESG?
ESG refers to the environmental, social, and governance factors that investors measure when analyzing a company’s sustainability efforts from a holistic view.
A term used to represent an organization’s corporate financial interests that focus mainly on sustainable and ethical impacts. It is used by capital markets to evaluate organizations and determine future financial performance.
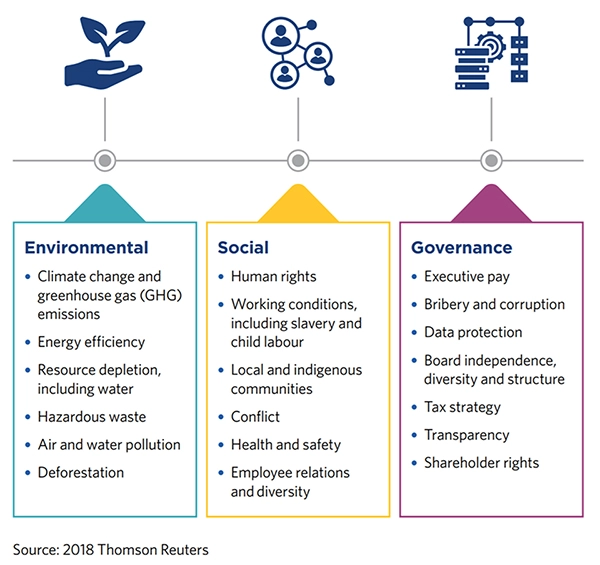
Significance of ESG

What data is used for ESG reporting?
The most common ESG reporting standards globally are as following:
1) Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
2) International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC)
3) Ask Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
– Carbon footprint reporting
– Water consumption reporting
– Climate risk disclosure
– Renewable energy reporting
– Stakeholder engagement
4) Climate Disclosure Standards Board (CDSB)
5) International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB)
6) Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
7) Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
8) Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP)
Significance of ESG reports
Investors and providers of capital are using ESG reports as a factor in their decision-making process. ESG reports provide transparency for investors and allow them to make more informed business decisions. It also helps businesses analyze and evaluate their impact on our world and help hold the companies accountable for their impact.
